Research Stories
Filter by category
Filter by year
Filter by year

Organic photovoltaics (OPVs) are a promising, economical, next-generation solar cell technology for scalable clean energy and wearable electronics. But the energy conversion loss due to the recombination of photogenerated charge carriers in OPVs has hindered further enhancement of their power conversion efficiency (PCE). Recently, researchers from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) overcame this obstacle by inventing a novel device-engineering strategy to successfully suppress the energy conversion loss, resulting in record-breaking efficiency.

A multinational team of researchers, co-led by a City University of Hong Kong (CityU) physicist, has found that a novel metallic crystal displays unusual electronic behaviour on its surface, thanks to the crystal’s unique atomic structure. Their findings open up the possibility of using this material to develop faster and smaller microelectronic devices.
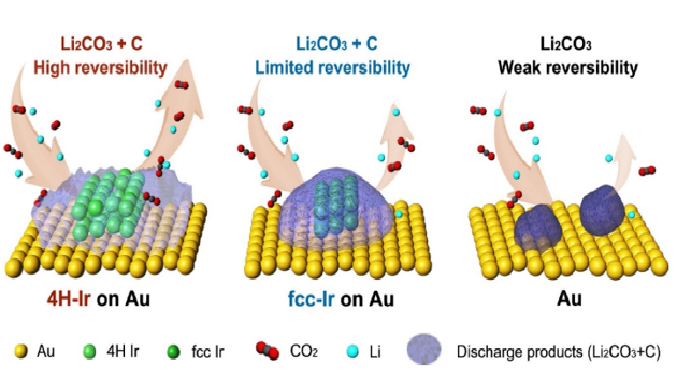
The metal-carbon dioxide battery is a promising and environmentally friendly technology, but its energy efficiency is limited. Recently, a research team co-led by chemists from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) discovered an innovative way to overcome this problem by introducing an unconventional phase nanomaterial as a catalyst, boosting battery energy efficiency up to 83.8%. The study reveals a novel design of catalysts for the new generation of meta-gas batteries that can contribute to carbon neutral goals.

The distinguished research capabilities of young scholars at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) are widely recognized. The National Natural Science Foundation of China recently announced the results of the Excellent Young Scientists Fund (Hong Kong and Macau) for 2022. Four young scholars at CityU were awarded. Each of them will receive a research grant of RMB 2 million to directly conduct innovative research in Hong Kong for a period of three years.

The double-helix structure of DNA deforms by environmental stimuli, which will then affect gene expression, and eventually trigger a sequence of cellular processes. Recent researches led by a physicist from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) observed substantial DNA deformations by ions and temperature changes. Furthermore, the researchers developed one simple physical model to explain DNA deformations. These results provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms of cellular responses to ions and temperature changes and can be used to control gene expression by ions and temperature.

A collaborative research team co-led by researchers from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) developed a new approach to generate deep-ultraviolet lasing through a “domino upconversion” process of nanoparticles using near-infrared light, which is commonly used in telecommunication devices.