The metal-carbon dioxide battery is a promising and environmentally friendly technology, but its energy efficiency is limited. Recently, a research team co-led by chemists from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) discovered an innovative way to overcome this problem by introducing an unconventional phase nanomaterial as a catalyst, boosting battery energy efficiency up to 83.8%. The study reveals a novel design of catalysts for the new generation of meta-gas batteries that can contribute to carbon neutral goals.
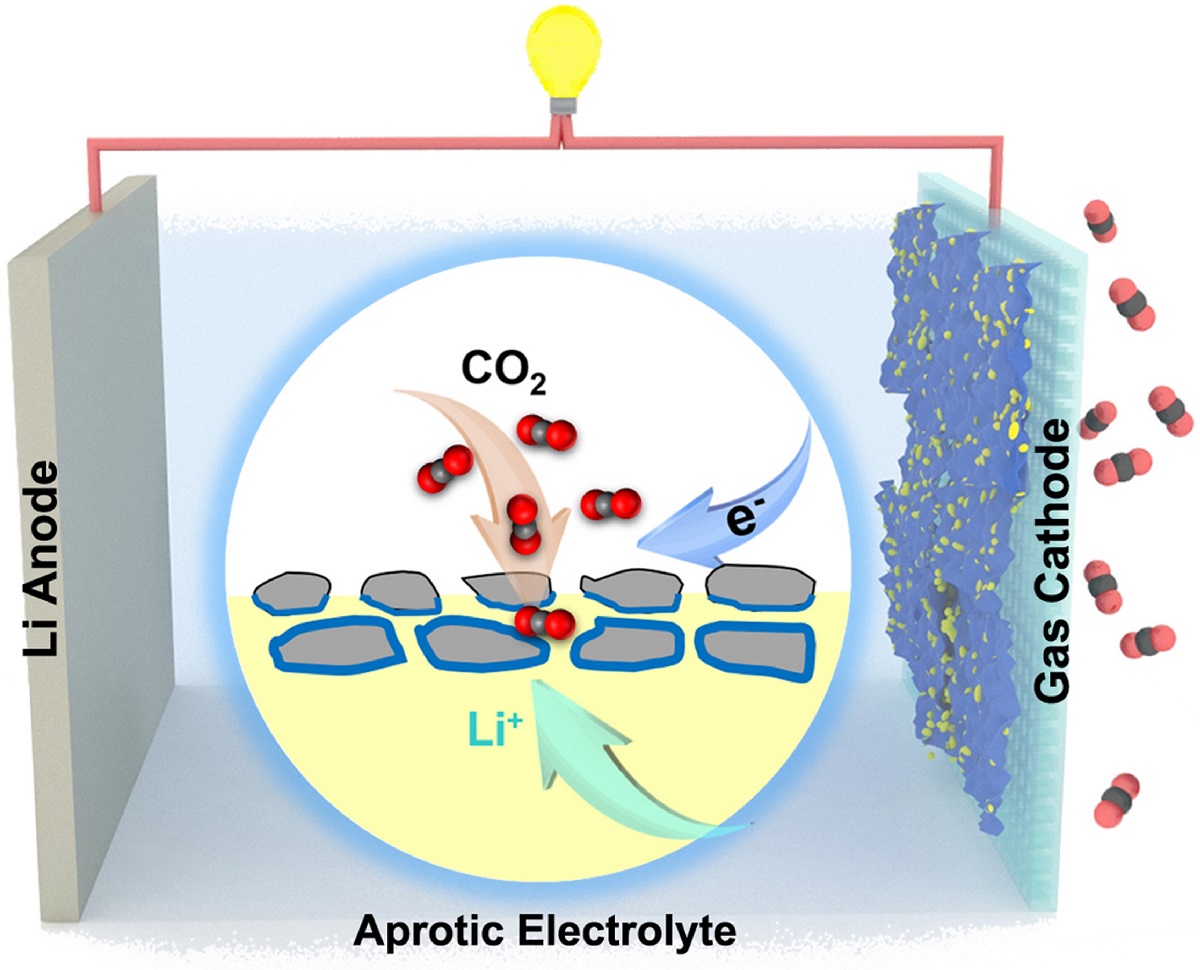
The metal-carbon dioxide battery can provide durable electricity (high energy density) for electronics, and enable carbon dioxide (CO2) fixation without extra energy consumption from an external circuit to convert CO2 greenhouse gas emissions into value-added products (Figure 1). In particular, the lithium-carbon dioxide battery has high theoretical energy density (1876 Wh kg-1), making it a promising candidate for next-generation high-performance energy conversion and storage technology.
However, metal-CO2 batteries still suffer from sluggish reaction kinetics. This causes large over-potential (i.e., more voltage or energy is required than is theoretical determined to drive the oxidation-reduction reaction that makes the battery work), low energy efficiency, poor reversibility, and limited cycling stability.
Technical hurdles in traditional catalyst modification strategies
“Researchers commonly consider morphology, size, constituents and distribution of metal-based components in composite cathode catalysts to be the main concerns that lead to differences in battery performance,” said Dr. Zhanxi Fan, Assistant Professor in the Department of Chemistry at CityU, and one of the leaders of the study. “But we found preparing novel catalysts with unconventional phases to be a feasible and promising strategy to boost the energy efficiency and performance of metal-gas batteries, especially since traditional modification strategies for catalysts have encountered long-term technical hurdles.”
Dr. Fan and his team accumulated extensive experience and knowledge related to the precise regulation of the crystal phase of metal-based nanomaterials, which enabled them to select suitable elements to construct their unconventional phases and subsequently study the effect of the crystal phase of catalysts on the reaction kinetics of a certain kind of aprotic (i.e., not involving hydrogen ions) metal-gas electrochemistry. “However, this does not mean that this process is easy to realize because it involves strict requirements on the bifunctionality of cathode catalysts in an organic environment,” explained Dr. Fan.
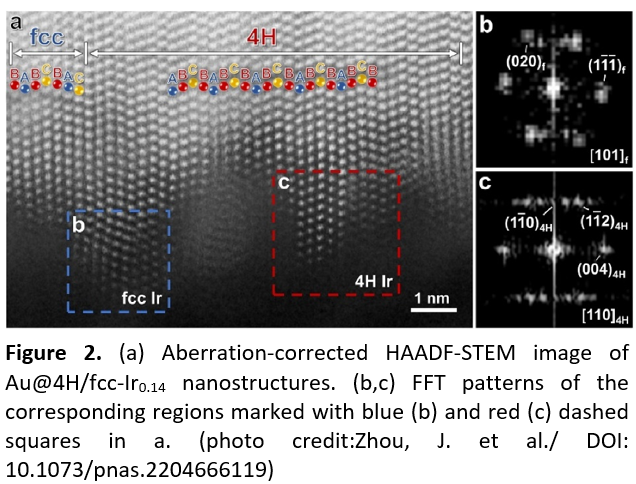
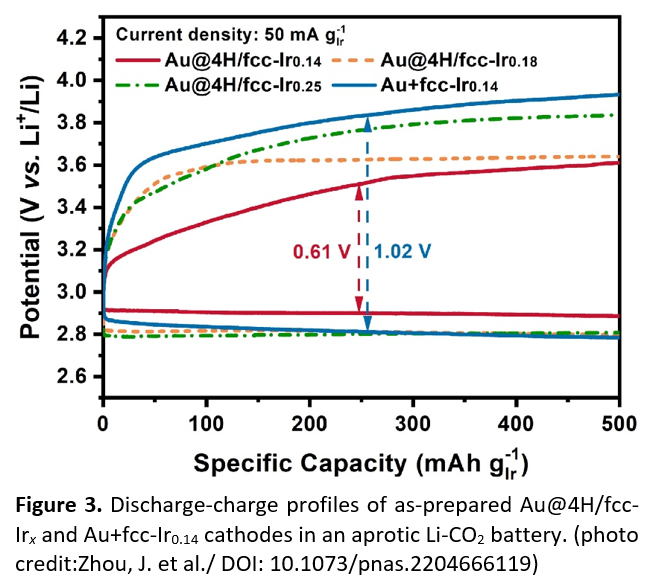
The team synthesized iridium nanostructures with an unconventional 4H/face-centred cubic (fcc) heterophase by controlling the growth kinetics of Ir on gold (Au) templates (Figure 2). In their experiments, the catalyst with 4H/fcc heterophase demonstrated a lower charge plateau (below 3.61 V) (Figure 3) and higher energy efficiency up to 83.8% during cycling in aprotic Li-CO2 batteries than other metal-based catalysts (commonly with charge potential of over 3.8 V and energy efficiency up to 75%).
Outstanding performance of unconventional phase metal nanomaterials
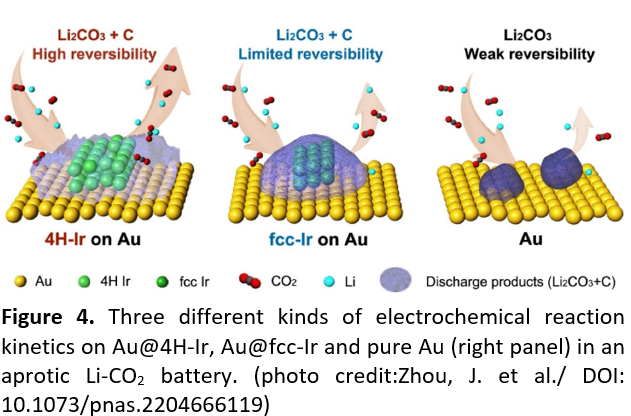
The combination of experiments and theoretical calculations conducted by the team revealed that 4H/fcc Ir nanostructures created through phase engineering are more favourable for the reversible formation of amorphous/low-crystalline discharge products (Figure 4), thereby lowering the overpotential and promoting the cycling stability of electrochemical redox reactions.
The unusual phase 4H/fcc Ir nanostructures performed much better than common fcc Ir, and achieved outstanding charge potential and energy efficiency compared to other reported metal-based catalysts used in aprotic Li-CO2 batteries.
“This study reveals the great potential of phase engineering of catalysts in metal-gas electrochemistry. It opens up a new direction to design catalysts for developing sustainable electrochemical energy conversion and storage systems,” concluded Dr. Fan.
The findings were recently published in the scientific journal The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) under the title “Boosting the reaction kinetics in aprotic lithium-carbon dioxide batteries with unconventional phase metal nanomaterials”.
The first authors are Mr. Jingwen Zhou and Dr. Lingwen Liao, from CityU, Dr. Tianshuai Wang from The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST), and Mr. Lin Chen from China Academy of Engineering Physics (CAEP). The corresponding authors are Dr. Zhanxi Fan, from CityU, Professor Tianshou Zhao, from HKUST, Professor Lin Gu, from the Institute of Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Professor Jianli Cheng, from CAEP. Other CityU team members include Professor Chun-Sing Lee, Dr. Bo Chen, Dr. Zhiqiang Guan, and a group of PhD students from the Department of Chemistry. The key funding sources were the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), the Innovation and Technology Commission (ITC) of Hong Kong, the Hong Kong Branch of the National Precious Metals Material Engineering Research Center (NPMM), and CityU.
This research article originated from CityU Research Stories.