A research team co-led by chemists from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) and Imperial College London (Imperial College) has developed new, highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. The breakthrough invention is expected to greatly accelerate the commercialisation of perovskite photovoltaic technology, providing a promising alternative to silicon solar cells.
Traditional solar cells are made of silicon, which has high power conversion efficiency and good stability. But they are relatively expensive and are reaching their practical and economic photovoltaic efficiency limits. Perovskites are regarded as the leading contender to replace silicon as the material of choice for solar panels. Perovskite solar cells are expected to cost less, have a low-manufacturing temperature, and are lightweight and flexible. They can be printed on plastic films as flexible solar cells, or can be used as window glass coating to absorb sunlight, offering wide usability.
Among the different types of perovskite solar cells, those with an inverted design configuration have exhibited exceptional stability, making them good candidates to reach the lifetime of commercial silicon solar cells. However, perovskite materials include chemically reactive components, which can easily volatilise and degrade under high temperature and humidity, shortening the solar cells’ operational lifetime. And there was still a lack of strategy to enhance the efficiency of inverted perovskite solar cells up to 25% to rival that of silicon solar cells, while maintaining their stability.

Credit: City University of Hong Kong
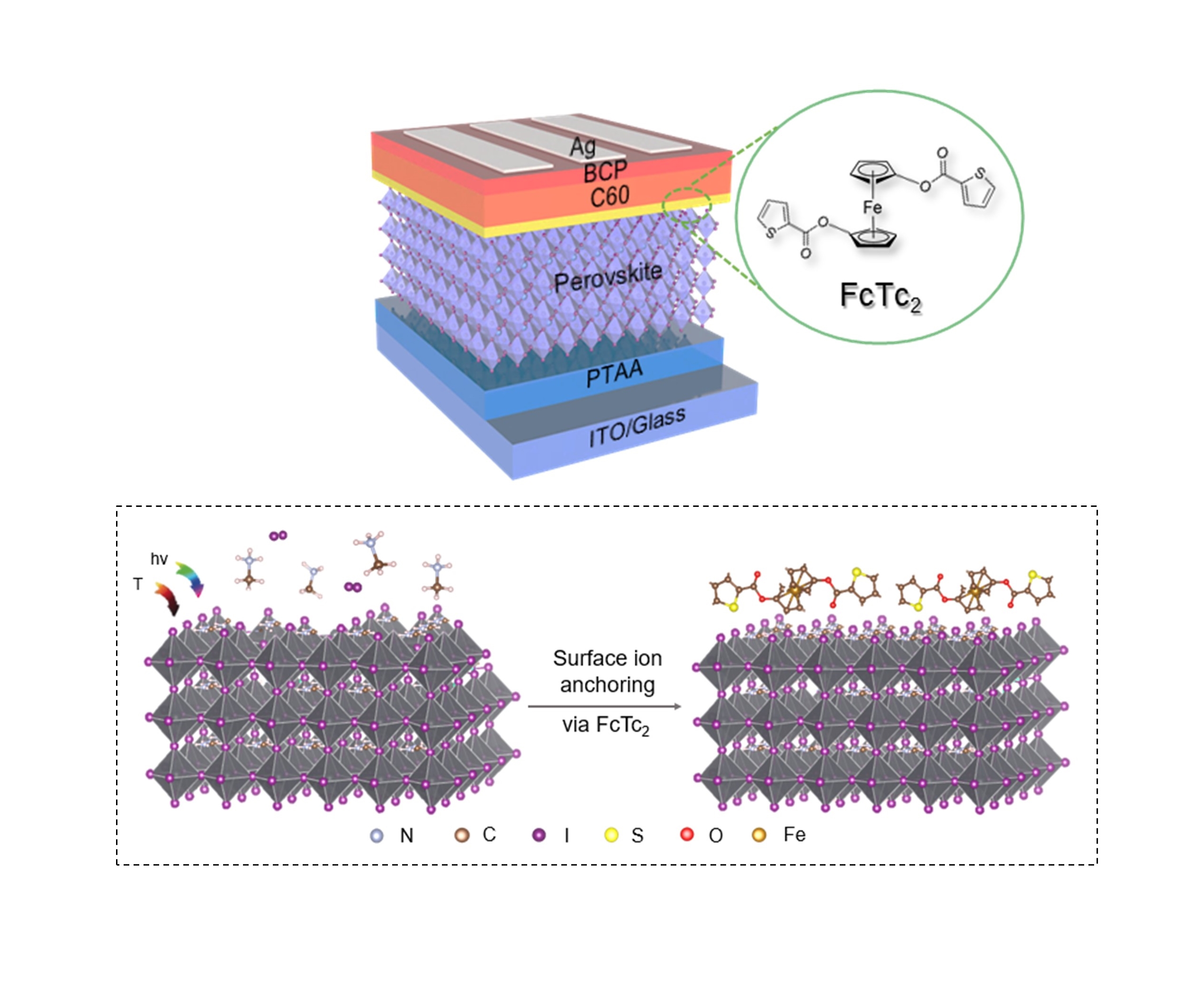
Inspired by the unique properties of a metal-containing materials called ferrocenes, Dr. Zonglong Zhu, Assistant Professor in CityU’s Department of Chemistry, overcame these obstacles with a new approach. In collaboration with Professor Nicholas Long from Imperial College, Dr. Zhu’s team ingeniously added ferrocenes to perovskite solar cells as an interface between the light-absorbing layer and the electron transporting layer, achieving a breakthrough. “We are the first team to successfully boost inverted perovskite solar cells to a record-high efficiency of 25% and pass the stability test set by International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC),” said Dr. Zhu.
The findings were published in the prestigious scientific journal Science under the title “Organometallic-functionalized interfaces for highly efficient inverted perovskite solar cells”.
“The unique properties of ferrocenes can help overcome the problems with perovskite solar cells,” said Professor Long, who is an expert in organometallic chemistry. Ferrocene is a compound with an iron atom “sandwiched” between two planar carbon rings. Dr. Zhu's team employed ferrocene, in which the carbon rings are attached to different organic groups, developed by Professor Long’s team. “These organic groups reduce the reactivity of the perovskite surface, enhancing both efficiency and stability,” Dr. Zhu explained.
Perovskite solar cells are made up of layers of materials. The perovskite layer is for light harvesting. The ferrocene molecules accelerate electron transfer from the perovskite active layer to the electrode in the electricity conversion layer, thus increasing efficiency.
(Source: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abo0039)
Another merit of these organic groups, explained Dr. Zhu is that “the ferrocene-based organometallic compound designed by the joint team firmly anchors the ion on the perovskite surface via a strong chemical bond, reducing the solar cells’ sensitivity to the external environment and delaying the device degradation process.”
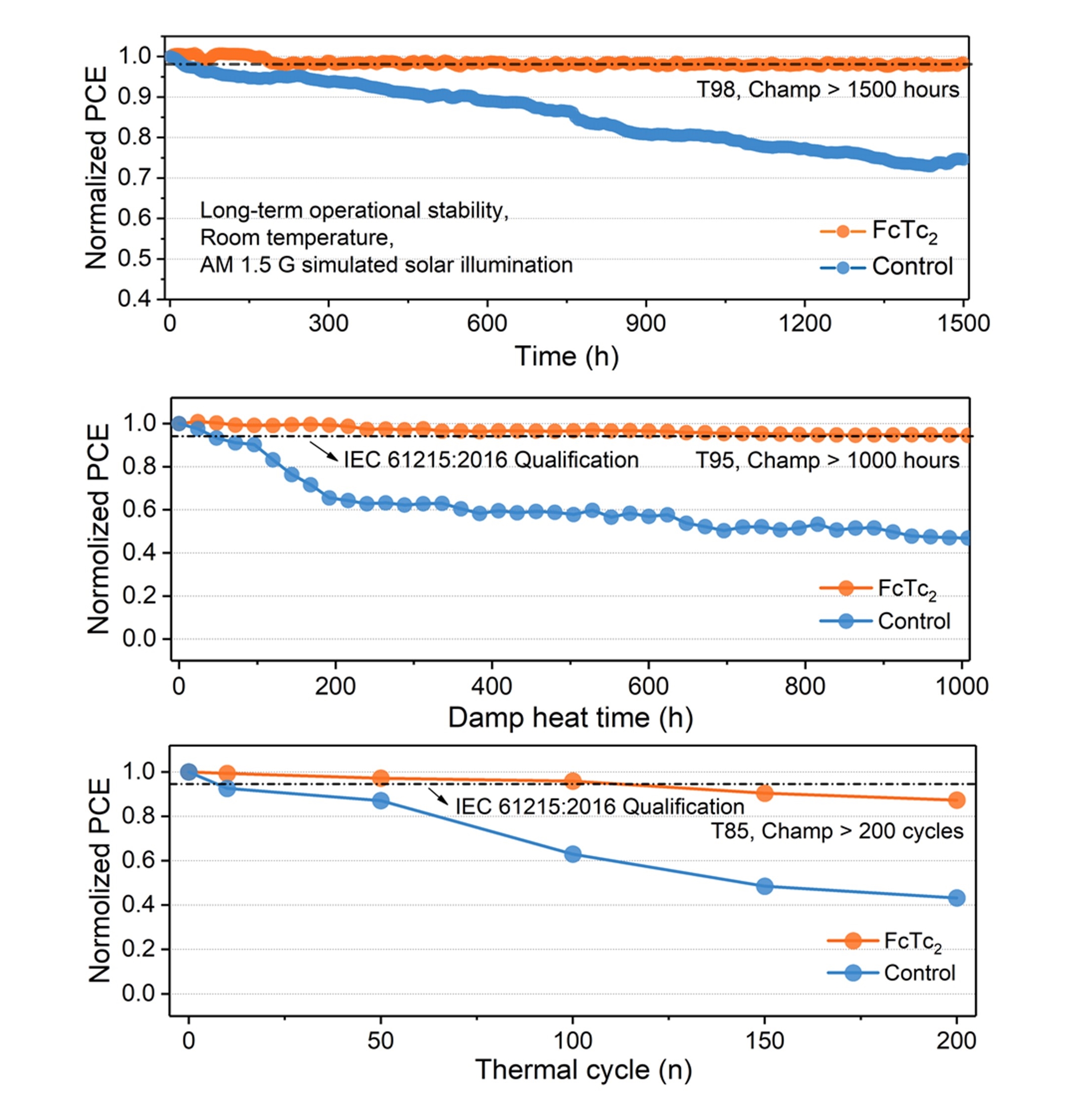
In the experiment, the CityU team found that these newly invented solar cells can run under continuous illumination for more than 1,500 hours and still maintain more than 98% of their initial efficiency. The devices also passed the international standard for mature photovoltaics, exhibiting superior stability in a hot and humid environment (85 degrees Celsius and 85% humidity).
“The most important part of this work is that we successfully fabricated highly efficient perovskite solar cells while providing promising stability. The reliable results mean that the commercialisation of perovskites is on its way,” said Dr. Zhu.
The collaboration team patented their design. “We aim to scale up the production of perovskite solar cells using this novel molecule and facile method, contributing to the global ‘zero-carbon’ sustainability goal,” concluded Dr. Zhu.

Dr. Zhu and Professor Long are the corresponding authors of the paper. The first authors are PhD students Zhen Li and Xin Wu and postdoctoral research fellow Dr. Bo Li, from the Department of Chemistry at CityU. Other CityU team members are Dr. Shoufeng Zhang and Mr. Danpeng Gao, from the Department of Chemistry.
The study was supported by the CityU Innovation and Technology Fund, the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province.
This research article originated from CityU Research Stories.
