CityU develops wireless, soft e-skin for interactive touch communication in the virtual world
Sensing a hug from each other via the internet may be a possibility in the near future. A research team led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently developed a wireless, soft e-skin that can both detect and deliver the sense of touch, and form a touch network allowing one-to-multiuser interaction. It offers great potential for enhancing the immersion of distance touch communication.
“With the rapid development of virtual and augmented reality (VR and AR), our visual and auditory senses are not sufficient for us to create an immersive experience. Touch communication could be a revolution for us to interact throughout the metaverse,” said Dr Yu Xinge, Associate Professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering (BME) at CityU.
While there are numerous haptic interfaces in the market to simulate tactile sensation in the virtual world, they provide only touch sensing or haptic feedback. The uniqueness of the novel e-skin is that it can perform self-sensing and haptic reproducing functions on the same interface.
Skin-patch device provides integrated functions for touch sensing and haptic reproduction
The e-skin contains 16 flexible actuators (cum sensors) in a 4 x 4 array, a microcontroller unit (MCU), a Bluetooth module and other electronics on a flexible circuit board. All the components are combined in a 7cm X 10cm, 4.2mm-thick skin-patch-like device.
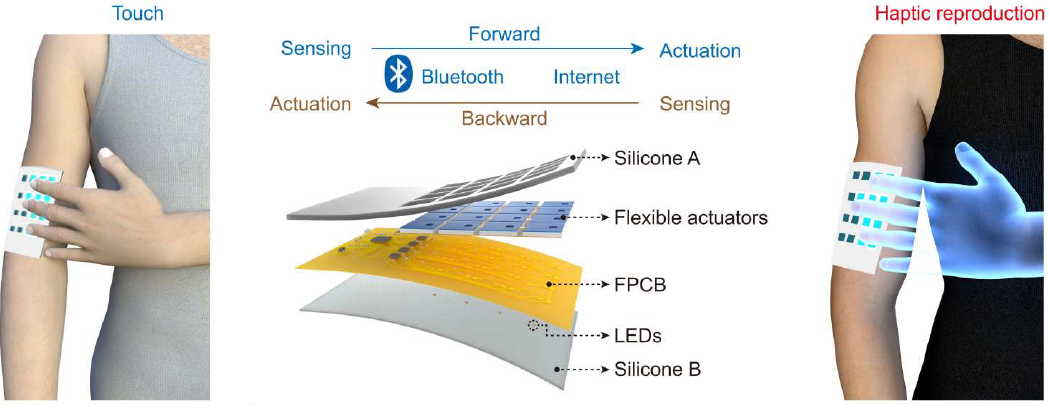
Credit: ? Li, D. et al. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.ade2450
The button-liked actuator, comparable in size to a HK 10-cent coin, serves as the core part of the e-skin. Each of the actuators consists of a flexible coil, a soft silicone support, a magnet and a thin polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) film, which perform the touch sensing and haptic feedback functions based on electromagnetic induction.
Once the actuator is pressed and released by an external force, a current is induced to provide electrical signals for tactile sensation to a corresponding actuator in another e-skin patch. The deeper the sender presses, the stronger and longer the sensation generated on the other e-skin.
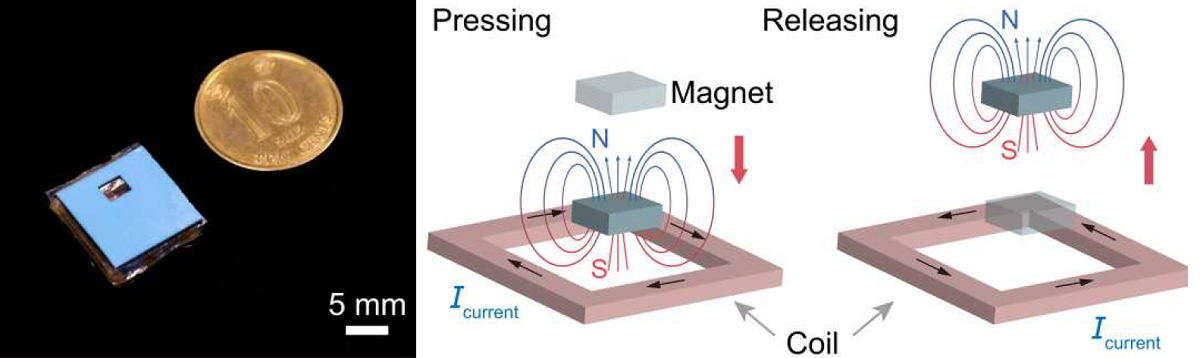
Credit: ? Li, D. et al. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.ade2450
The electrical signal generated from the actuators is converted to a digital signal by an analog-to-digital converter on the circuit board of the e-skin patch. The data is then transmitted to the actuators on another e-skin via Bluetooth.
When the signal is received, a current is induced to reproduce the haptic feedback on the receiver’s e-skin through mechanical vibration. The process can be reversed to deliver vibrations from the receiver’s e-skin to the corresponding actuator of the sender’s.
Although each actuator can perform only one task at a time, the rest of the 15 actuators on the e-skin can supplement each other and perform the sensing or haptic reproducing function, allowing the e-skin patch to achieve bidirectional touch transmission simultaneously.
Touch IoT offers a wide range of potential applications

Credit: ? Li, D. et al. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.ade2450
“Our e-skin can communicate with Bluetooth devices and transmit data through the internet with smartphones and computers to perform ultralong-distance touch transmission, and to form a touch Internet of Things (IoT) system, where one-to-one and one-to-multiple touch delivery could be realised. Friends and family in different places could use it to ‘feel’ each other,” said Dr Yu. “This form of touch overcomes the limitations of space and greatly reduces the sense of distance in human communication.”
Next, the research team will focus on practical applications for people with visually impairment, who could wear the e-skin to gain remote directional guidance and read Braille messages.
The research findings were published in the scientific journal Science Advances under the title “Touch IoT enabled by wireless self-sensing and haptic-reproducing electronic skin”.

Credit: ? Li, D. et al. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.ade2450
The first co-authors are Dr Li Dengfeng, then-postdoc on Dr Yu’s research team, Dr Yao Kuanming, postdoc in BME, Mr Zhou Jingkun and Mr He Jiahui, both PhD students in BME at CityU, and Ms Liu Sitong from Dalian University of Technology (DUT). The corresponding authors are Dr Yu, Professor Xie Zhaoqian from DUT, and Dr Dai Yuan from Tencent Robotics X. The research was supported by CityU and the Hong Kong Research Grants Council.
Related Stories:
A wirelessly-controlled and wearable skin-integrated haptic VR device