Data science model emphasises the need for social distancing to combat Covid-19

Researchers at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) found that school closures are not as effective as social distancing in public facilities for controlling Covid-19 in New York City (NYC).
A new mathematical model, which has been developed by Dr Zhang Qingpeng, Associate Professor in the School of Data Science (SDSC) at CityU, examines the effectiveness of various non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) in NYC in reducing the total number of infections and deaths among various age groups and locations for the period of January to December 2020.
This city-specific model can provide novel insights for other cities, according to their unique age and location mixing patterns.
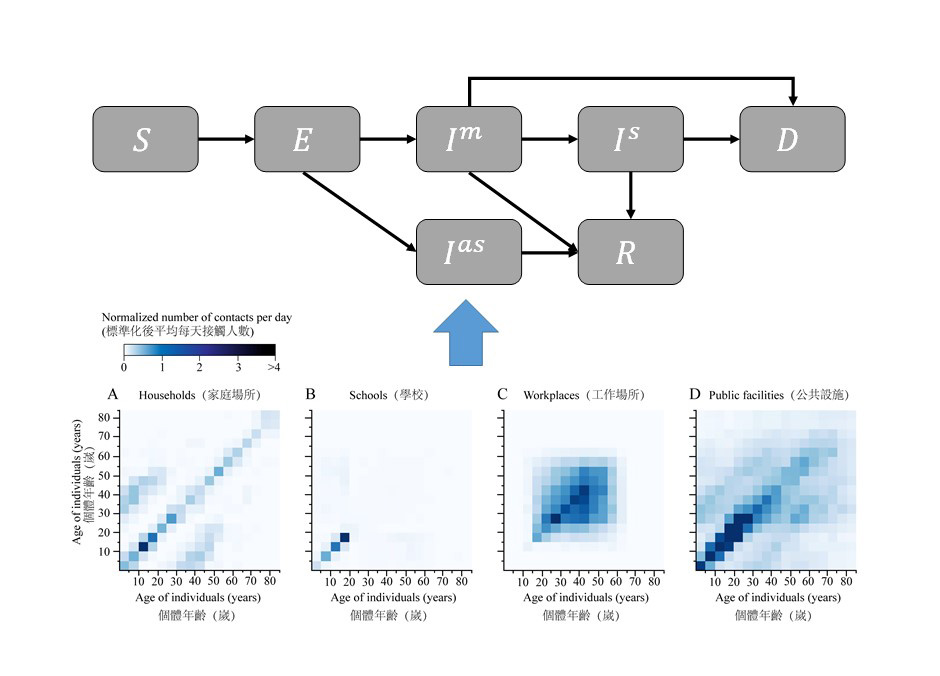
The NPIs include no intervention, school closures, social distancing for the entire population, social distancing for those aged over 64, and adaptive policies such as full lockdowns.
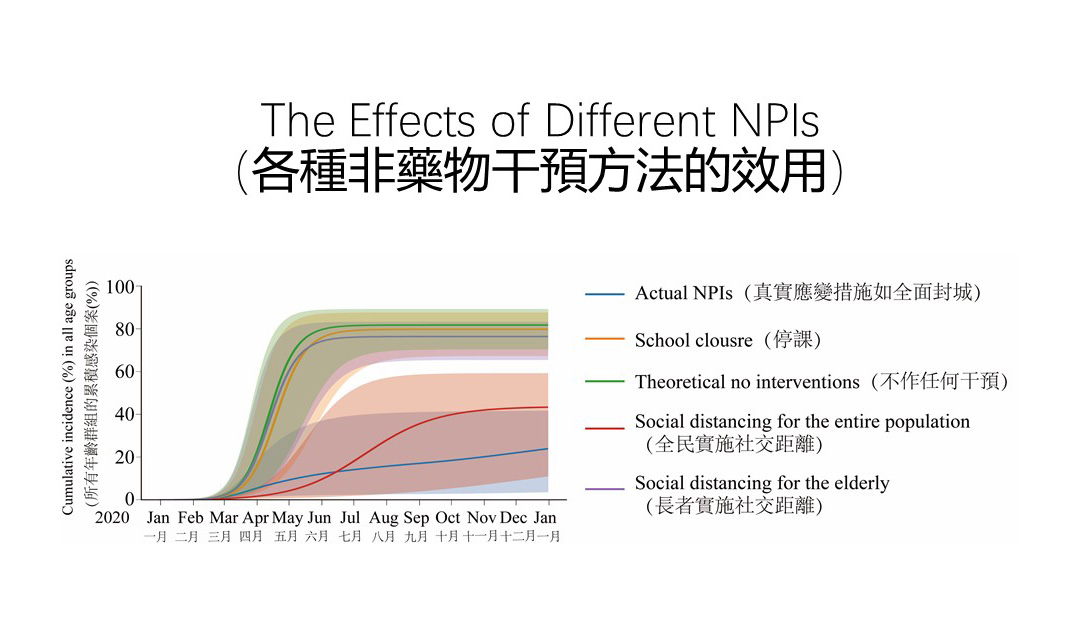
The results of the experiment show that control policies implemented in NYC reduced the number of infections by 72% and the number of deaths by 76% by the end of 2020.
Among all the NPIs, the results show that social distancing, in the form of reducing contact on public transport, banning public gatherings and the protection of the elderly in public facilities, is the most effective control measure. It reduces the number of infections by 47% and the number of deaths by 51% across society, and reduces the number of both infections and deaths among the elderly by 47%.
Meanwhile, city-wide school closures may not work as effectively in terms of reducing the number of deaths, resulting in only a 4% reduction in the number of infections compared with the no-intervention policy.
The study implies that NPIs can contain the epidemic with minimal disruption to social contacts in the city, which is particularly important for cities like NYC and Hong Kong, whose economies rely on international trade.
“To confront the Covid-19 pandemic, novel and transparent data science approaches are essential for characterising population demographics, human movement and economic activities,” said Dr Zhang.
Dr Zhang and Professor Daniel Zeng Dajun of the Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CASIA) are the corresponding authors of the paper. The other collaborators are Professor Dirk Pfeiffer of the Department of Infectious Diseases and Public Health at CityU, Yang Jiannan, PhD student at the SDSC, Professor Cao Zhidong of the CASIA, Dr Gao Jianxi and Dr Zhong Lu of the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in New York. Dr Zhong is a PhD graduate of the SDSC.