Latest Research
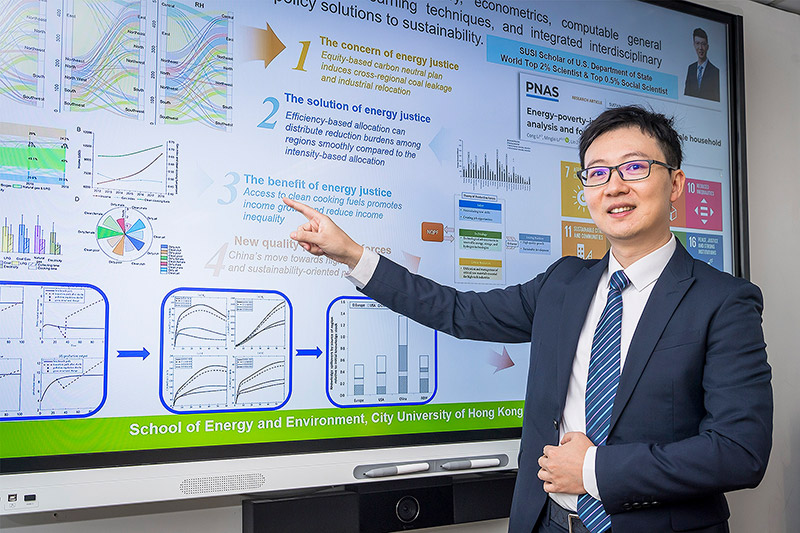



Clean cooking fuels have great potential to reduce income inequality, CityUHK researchers find
Dedicated to achieving the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), researchers at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) discovered that transitioning to clean cooking fuels can significantly promote multiple SDGs, including affordable and clean energy (SDG 7), poverty elimination (SDG 1) and reduced inequality (SDG 10).
Using data from Chinese households, the team found that a 10% increase in clean cooking fuel use could boost total annual household income by US$37 billion. This income growth is more significant for lower-income groups, helping to reduce income inequality.
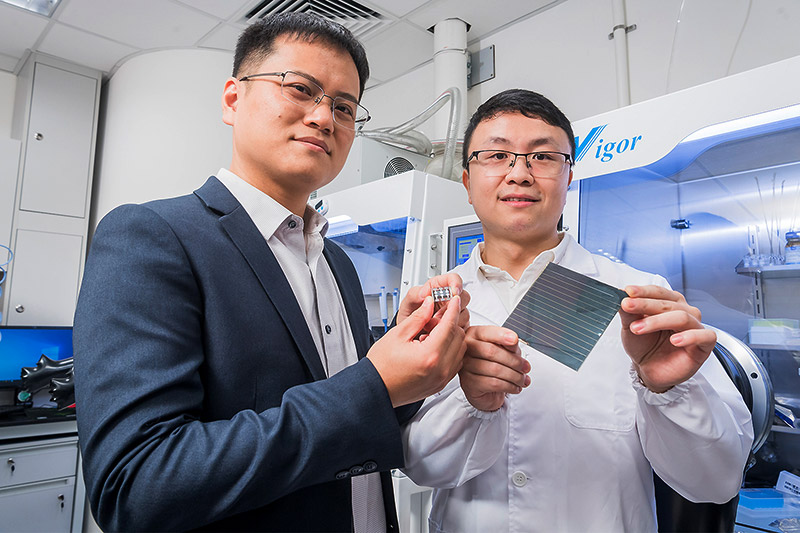

Interdisciplinary science research for enhancing sustainability through solar cells
Drawing on an array of interdisciplinary science research and knowledge, a new fabrication technique for substantially enhancing the prospects of commercialising perovskite solar cells through improved stability, reliability, efficiency and affordability is underway at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK).
Published in Science, the research is significant because the simple device structure that the CityUHK team has built can facilitate future industrial production and enhance confidence in the commercialisation of perovskite solar cells.
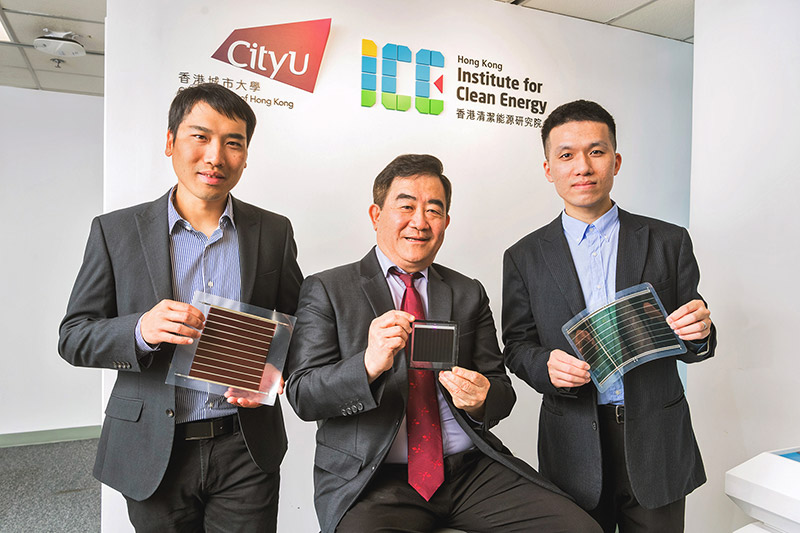


Highly efficient and stable solar cells can now be mass produced like printing newspapers
Scientists at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) have made continuous breakthroughs in photovoltaic energy, developing highly efficient, printable and stable perovskite solar cells to achieve carbon neutrality and promote sustainable development.
The new type of perovskite solar cells can be mass-produced at a speed comparable to newspaper printing, with a daily output of up to 1,000 solar panels. Owing to their flexible, semi-transparent characteristics, they can also be made into light-absorbing glass windows, realising the concept of “urban solar farms” in cities with many high-rise buildings, such as Hong Kong and Shenzhen.



CityUHK collaborates in groundbreaking research to track livestock disease threats and support smarter One Health interventions
Professor Dirk Pfeiffer, Chow Tak Fung Chair Professor of One Health and Director of the Centre for Applied One Health Research and Policy Advice at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK), has collaborated with a team of interdisciplinary scientists from the Global Challenges Research Fund (GCRF) One Health Poultry Hub to develop a cutting-edge computer tool that enables the mapping and tracking of avian influenza virus spread across time and space. This significant breakthrough will allow decision-makers to better understand infectious disease threats associated with global food systems and more effectively target actions and interventions to minimise risk.
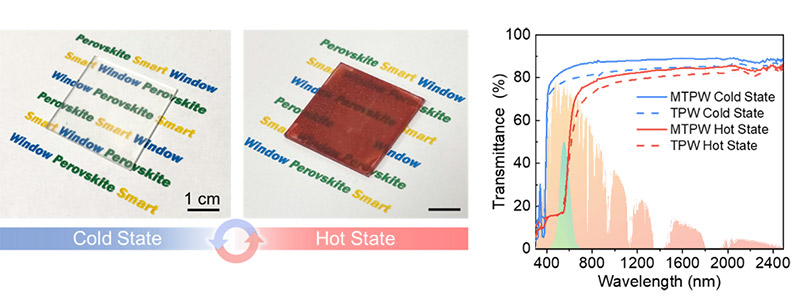


CityUHK researchers develop mask-inspired perovskite smart windows to enhance weather resistance and energy efficiency
Thermochromic perovskite is a new color switch material used in energy-saving smart windows. Despite its potential for energy savings, thermochromic perovskite suffers from poor weather resistance, susceptibility to water damage, and high optical haze, limiting its practical application. To overcome these challenges, researchers from City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) developed a breathable, weather-resistant, low-haze perovskite smart window inspired by medical masks, pushing forward the wide applications of smart windows in green buildings.
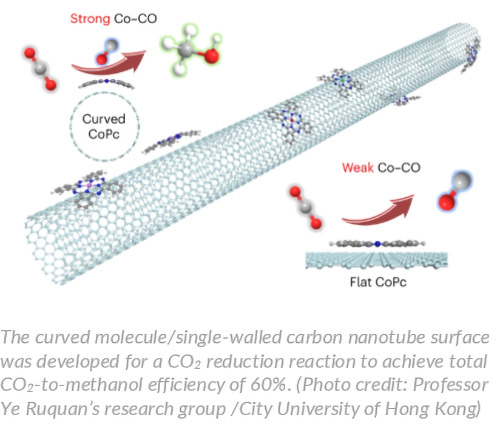

Curved carbon nanotubes enhance electrocatalysts for carbon neutrality
Electrocatalysis plays a vital role in developing clean energy, greenhouse gas removal and energy storage technologies. A study co-led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) researchers found that single-walled carbon nanotubes are excellent substrates for enhancing greenhouse gas conversion through molecular curvature. By using these nanotubes as support to induce strain on an electrocatalyst, the efficiency of carbon dioxide reduction to methanol can be significantly improved. This breakthrough opens avenues for developing curved molecular electrocatalysts to efficiently convert carbon dioxide (CO2), one of the key greenhouse gases, into useful chemicals and fuels, thus reducing carbon emission.