A research team co-led by Dr Geoffrey C. Y. Lau, Assistant Professor at the Department of Neuroscience, City University of Hong Kong (CityU), has recently identified and developed a new drug for treating temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE).
TLE is one of the most common types of epilepsy worldwide. Although patients can be treated by existing medications, many of them remain unresponsive to drug treatment. Hence, new medications and drug targets are needed. Connexin-based gap junctions and hemichannels in brain glial cells are implicated in TLE, but blocking gap junctions can lead to undesirable side effects.
Dr Lau’s research group identified a new small-organic molecule called D4, which selectively blocks connexin hemichannels (but not gap junctions). They investigated its effect in treating TLE using a mouse model. Dr Lau’s team found that D4 strongly suppresses the TLE-induced neuroinflammation, curbs TLE seizures, and increases animal survival rate.
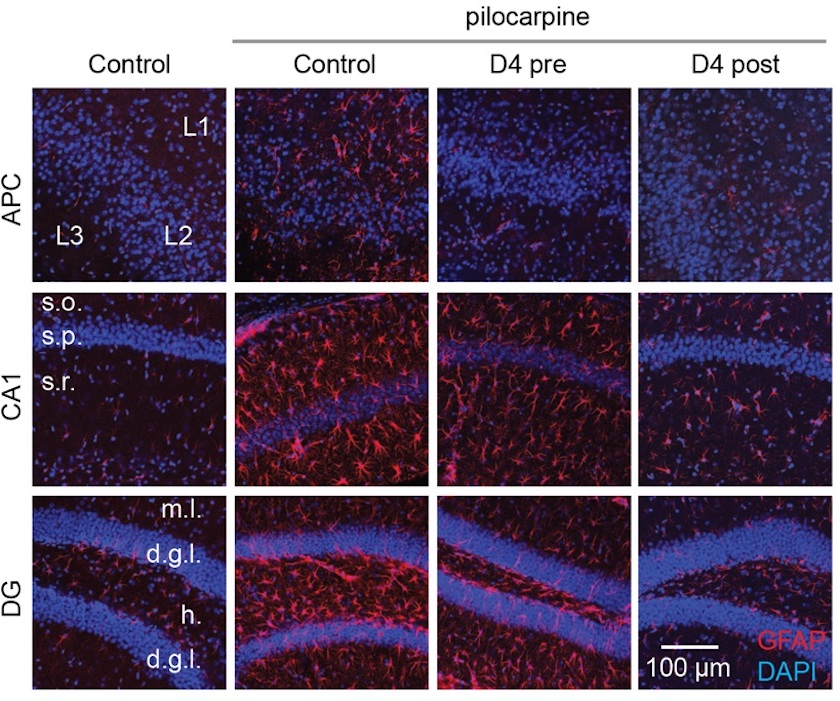
This research is the product of a collaboration between the corresponding authors, Dr Geoffrey Lau (CityU Neuroscience) and Dr Juan C Saez (University of Valparaíso, Chile). The findings entitled, “Inhibition of connexin hemichannels alleviates neuroinflammation and hyperexcitability in temporal lobe epilepsy”, is published at a leading international journal, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) (https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2213162119).
The first author is Dr Anni GUO, a postdoc in Dr Lau’s lab who graduated and obtained her PhD from CityU’s Interdisciplinary PhD Programme in Veterinary Medicine in collaboration with Cornell University. Funding on the CityU side is provided by the Hong Kong Research Grants Council (ECS 21103818, GRF 11104320 and GRF 11104521 to C.G.L.), Shenzhen General Basic Research Program (JCYJ20190808182203591 to C.G.L.), a grant from ITF-InnoHK, and internal funds from City University of Hong Kong (to C.G.L.).
News Coverages
CityU Research Stories
CityU neuroscientists discover a new drug candidate for treating epilepsy
城大研究
城大神經(jīng)科學(xué)家發(fā)現(xiàn)治療癲癇的新候選藥物
香港城大研創(chuàng)
香港城大神經(jīng)科學(xué)家發(fā)現(xiàn)治療癲癇的新候選藥物
Nature Reviews Neurology
Targeting connexin hemichannels to treat temporal lobe epilepsy
邏輯神經(jīng)科學(xué) (Logical Thinking Neuroscience)
PNAS︱劉俊宇團(tuán)隊(duì)揭示連接蛋白半通道在減輕顳葉癲癇發(fā)病過(guò)程中的神經(jīng)炎癥和過(guò)度興奮的重要作用
EurekAlert!
CityU neuroscientists discover a new drug candidate for treating epilepsy